Preamble
这里讲到的 Trie 树按照如下规则定义。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
const int alpha_size = 26;
const int maxn = (1 << 10) - 1;
struct TrieNode {
int next[alpha_size]; // TrieNode.next[X] 指向本节点经过 X
// 字符边走到的下一个节点
int fail; // 给 AC 自动机用的,指向回跳边的终点。
int is_termination; // 该节点是否是某个字符串的终点?是则标记为 1,否则标记为
// 0. 不用 bool 是因为 AC 自动机要用特殊标记。
TrieNode() {
memset(next, 0, sizeof next);
fail = -1; // 一开始没有东西
is_termination = 0;
}
};
struct Trie {
TrieNode nodes[maxn];
int ctr; // 有多少个节点
Trie() : ctr(0) {}
void insert(string s) {} // ...
};
|
AC 自动机
边?
AC 自动机引入的两个概念是 回跳边 与 转移边。
总之先放张图在这里:
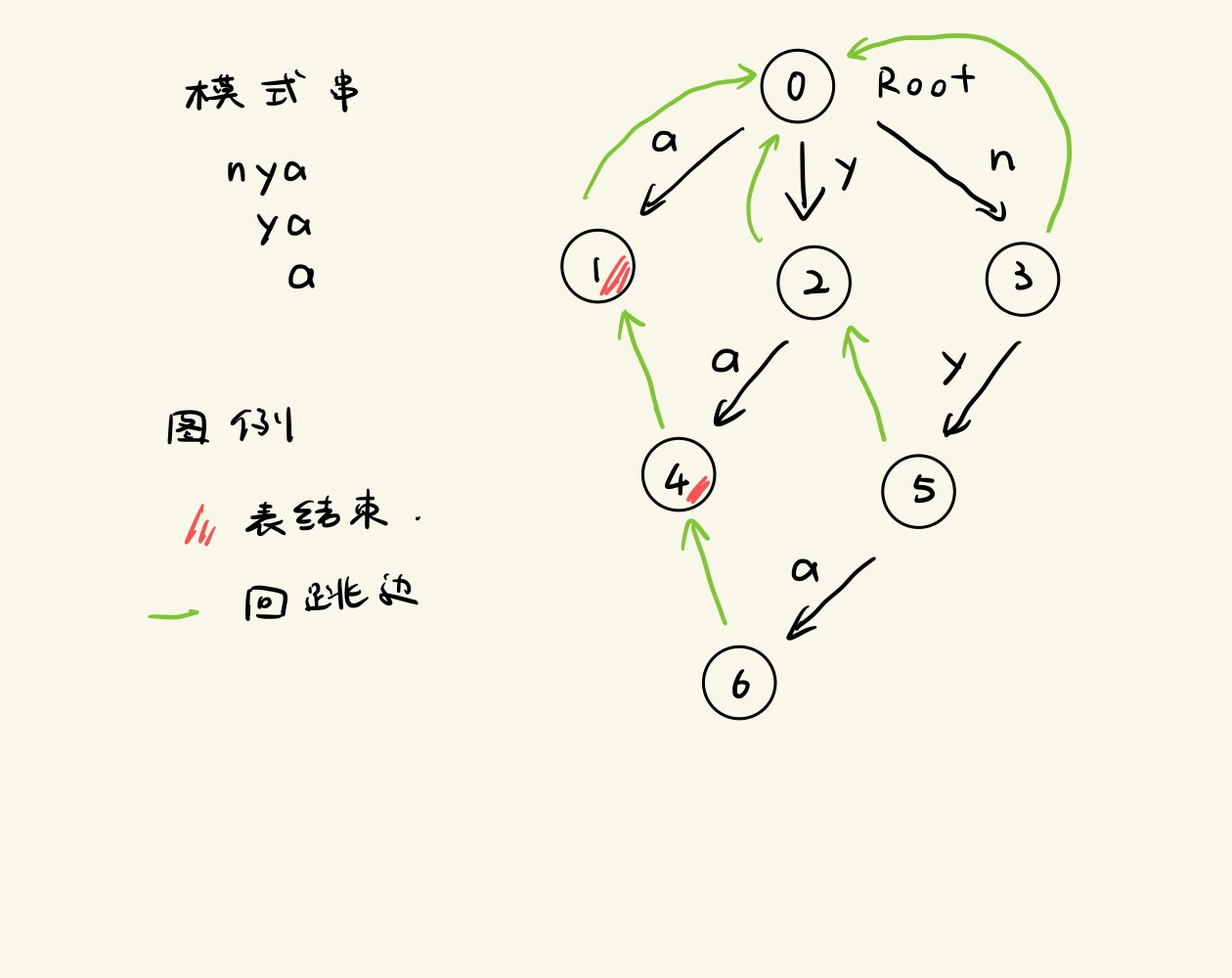
所指节点必定是当前节点的最长后缀。这是比较好理解的,比如节点 #6 的回跳边指向 #4 (“ya”),即为当前节点 (“nya”) 的最长后缀。
所指节点一定是当前节点的最短路。
大概理解了一下:由于讲的 query 函数中采用双指针,$i$ 指针从来不回退,所以在没有匹配的时候(例如 nyae 中的 e 显然不与任何模式串匹配(需要回退到节点 #0),或 nyay 中, y 虽然是模式串 ya 的一部分,但是按照设定, $i$ 不能从节点 #6 一路回退到节点 #0 (Root),再从 #0 转移到节点 #2。所以需要维护一堆转移边,这样可以实现 $i$ 指针从来不回退的算法。)
按照我的理解,这里的「回退」指的是「按照原来的路反方向走」,例如 nyae 中在处理 e 前 $i$ 指针实际上在 #6 处,一路找回 #0 实际上是麻烦的,所以直接找到最短路让 #6 「往前走」跳到 #0 不算「回退」。
建!
讲了这么多,是时候该建设一个 AC 自动机了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
struct ac_automaton {
Trie t;
void build() {
// 使用 BFS 建立 AC 自动机
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
// 这里的 26 是因为只需要处理 26
// 个小写英文字母,如果有别的字母表,那就按字母表的来
if (t.nodes[0].next[i]) {
// 把根节点的所有儿子入队
q.push(t.nodes[0].next[i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int c = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
// 建边
if (t.nodes[c].next[i]) {
// 有儿子,则这个儿子的父节点就是本节点
t.nodes[t.nodes[c].next[i]].fail = t.nodes[t.nodes[c].fail].next[i];
// 继续对儿子进行处理
q.push(t.nodes[c].next[i]);
} else {
// 没这个儿子,那就建转移边
t.nodes[c].next[i] = t.nodes[t.nodes[c].fail].next[i];
// 这玩意其实相当于一个 Trie 的特殊规则感觉(
}
}
}
}
};
|
查!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
int query(string s) {
// 这个 query 是查询 s 中「出现过的不同模式串个数」!
int ans = 0;
for (int k = 0, i = 0; s[k]; k++) {
i = t.nodes[i].next[s[k] - 'a'];
for (int j = i; j && (~(t.nodes[j].is_termination)); j = t.nodes[j].fail) {
// 解释一下这个循环条件:
// j: 如果 j 指针回到了根节点(不代表任何字符串,或者理解为代表一个空字符串),则退出循环
// ~(t.nodes[j].is_termination): ~ 运算符表示按位取反。
// 这个玩意就非常刁钻了,我们好↓好↑分析一下捏:
// 无论 is_termination = 0 还是 1, 按位取反都 > 1(按照二进制表述,大小关系在 unsigned int 环境下讨论),所以可以继续跳
// 如果 is_termination = -1,则按位取反直接 = 0, 表示这个节点已经被统计过,不再纳入统计范围之内,也不跳了,直接退出循环。
// 下面这个 += 也是一样,如果 is_termination = 0,则这个节点不是模式串终点,不统计到答案中;否则统计到答案中。
ans += t.nodes[j].is_termination, t.nodes[j].is_termination = -1;
}
}
return ans;
}
|
写!
做道题试试咯。
P3796,拿下!
附代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
|
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 71 + 1e5;
struct trienode {
int next[26];
int fail = 0;
int is_termination = 0;
string represent = "";
trienode() { memset(next, 0, sizeof next); }
};
struct ac_automaton {
trienode tr[maxn];
int ctr = 0;
map<string, int> mp;
ac_automaton() { mp.clear(); }
void insert(string s) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int c = s[i] - 'a';
if (!(tr[p].next[c])) {
tr[p].next[c] = ++ctr;
tr[tr[p].next[c]].represent = tr[p].represent + s[i];
}
p = tr[p].next[c];
}
tr[p].is_termination = 1;
mp[s] = 0;
return;
}
void build() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (tr[0].next[i])
q.push(tr[0].next[i]);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (tr[u].next[i]) {
tr[tr[u].next[i]].fail = tr[tr[u].fail].next[i];
q.push(tr[u].next[i]);
} else {
tr[u].next[i] = tr[tr[u].fail].next[i];
}
}
}
return;
}
void query(string s) {
for (int k = 0, i = 0; s[k]; k++) {
i = tr[i].next[s[k] - 'a'];
for (int j = i; j; j = tr[j].fail) {
if (tr[j].is_termination) {
mp[tr[j].represent]++;
}
}
}
return;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
string pattern, query;
vector<string> patterns, answers;
while (1) {
cin >> n;
if (n == 0) {
break;
}
ac_automaton a;
patterns.clear();
answers.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> pattern;
a.insert(pattern);
patterns.push_back(pattern);
}
a.build();
cin >> query;
a.query(query);
int local_max = 0;
for (string s : patterns) {
if (a.mp[s] > local_max) {
local_max = a.mp[s];
answers.clear();
answers.push_back(s);
continue;
}
if (a.mp[s] == local_max) {
answers.push_back(s);
}
}
cout << local_max << endl;
for (string s : answers) {
cout << s << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
|
